Mid-year review 2023 - Sustainable Future: Resurgence on the horizon
27 June 2023
Despite the hurdles encountered in the first half of the year, a strong recovery is anticipated in the cleantech sector during the latter half, owing to the pickup in consumer demand, declining key input costs, and the expected impact of the landmark government investment plans signed last year.
Bottom line
The first half of 2023 presented a challenging landscape for our cleantech investment strategy, particularly due to a slowdown in China's EV and battery space. However, this trend is now showing signs of a turnaround, with increasing demand expected to stimulate growth in the second half of the year. This anticipated resurgence is set to invigorate the entire value chain, benefiting our major areas of exposure and underpinning our positive outlook for the rest of the year.
At the same time, we are closely watching the unfolding of major governmental climate plans announced last year, including the U.S's Inflation Reduction Act and Europe's REPowerEU plan. The details of these multibillion-dollar plans, which are yet to be fully revealed, are anticipated to provide significant market momentum in the forthcoming quarters, stimulating the global cleantech sector and potentially generating significant opportunities.
Table of contents
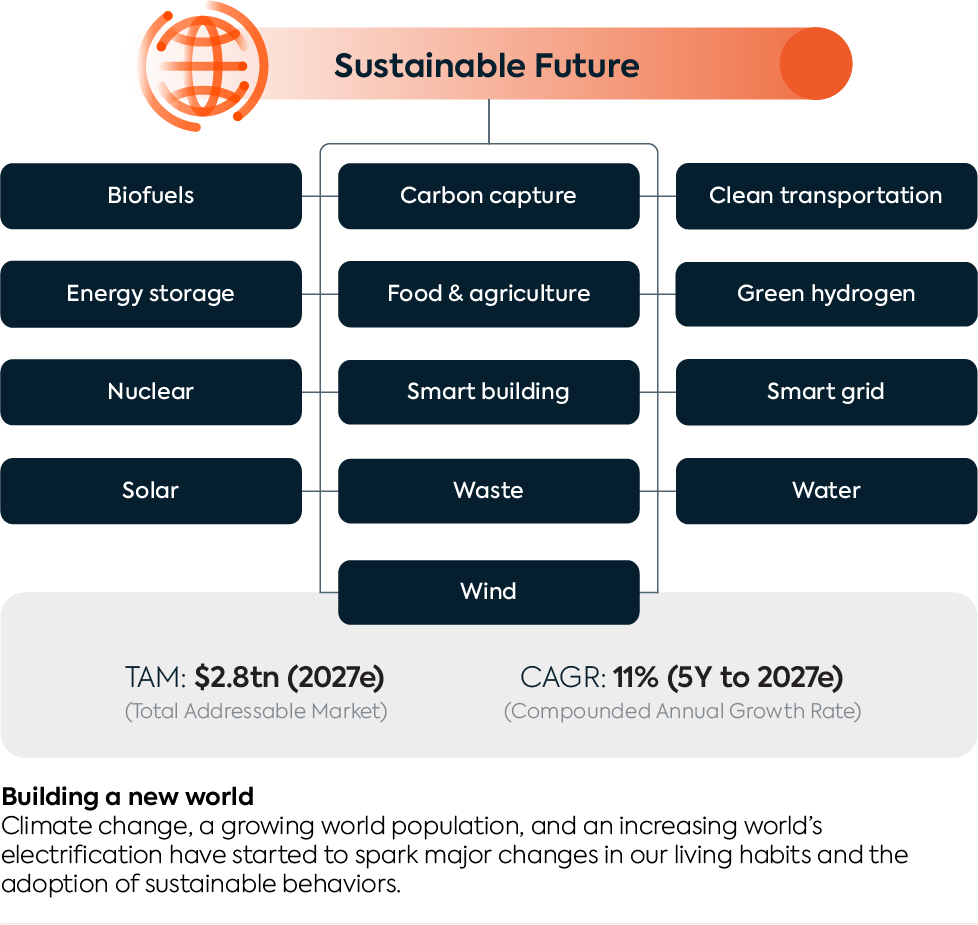
Portfolio Snapshot
Sustainable Future Overview
Energy Storage
Clean Transportation
Solar
Smart Grid
Wind
Biofuels
Smart Building
Water
Hydrogen
Food & Agriculture
Nuclear
Carbon Capture
Waste
Year favourites 2023 – An update
Catalysts/Risks
Portfolio Snapshot
Overview
Resurgence on the horizon
A difficult first half for China
China's cleantech sector experienced a challenging start to the year,
Following over two years of stringent lockdowns and a zero-COVID policy, China reopened at the end of last year, fostering expectations of a consumer-led demand rebound. Although post-reopening there was a noticeable surge in "revenge spending" in areas such as travel and home furnishing, many industries struggled to fill the gap between high expectations and a slower-than-anticipated recovery.
This was particularly evident in the electric vehicle industry, which faced a slowdown in the early part of the year, driven by the phase-out of government subsidies. Any deceleration in this fast-growing sector significantly affects the upstream supply chain, leading to production cutbacks in response to diminished demand.
However, demand has shown signs of rebounding since May, and we anticipate this will positively affect all segments of the supply chain. Eventually, consumer spending will likely transition towards more expensive items. As for renewable energy expansion, the Chinese government in its most recent five-year plan has placed considerable emphasis on accelerating its development. We anticipate that both solar and wind energy sectors will achieve double-digit growth in 2023.
Input cost stabilization
In our 2023 outlook, we highlighted that crucial input prices such as steel (an essential component for solar panels and wind turbines) and container freight costs had begun to descend, and are now back to pre-Covid levels.
Many significant cost components that are vital for the clean technology sector, including but not limited to polysilicon (-60% YTD), lithium (-40% YTD), or aluminum (-40% from its highs) have also been on a consistent downward trajectory.
We anticipate that the normalization of the supply chain, fostered by this widespread cost stabilization, will continue to relieve margin pressure and stimulate the adoption of clean technology.
Government to start paying out planned subsidies
Last year witnessed the signing of some of the most extensive climate plans to date, namely the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in the U.S and the REPowerEU plan in Europe. These expansive investment plans, worth several hundred billion dollars/euros, are still being refined and detailed by government agencies.
More specifically, the U.S. Department of the Treasury and the IRS continue to release guidance on domestic content requirements that will determine eligibility for additional subsidies impacting the solar, wind, and battery industries. In Europe, the Net Zero Industry Act and the Critical Raw Material Act are establishing targets, which we anticipate will be followed by more detailed plans from individual countries. Despite this, we believe the market has not yet fully accounted for the impact of these multibillion-dollar plans. We expect them to start materializing and influencing companies' operations in the near future.
The heartbeat of transition
LFP gaining interest in the battery space
In the sector of energy storage and electric vehicle batteries, lithium-ion technology continues to lead, as stated in our 2023 outlook. The primary chemistries for these batteries, LFP and NMC, are undergoing a shift. LFP, while less energy-dense, is cheaper and has a longer lifespan. Consequently, it's garnering increased attention, with factors like the Russia-Ukraine conflict affecting battery-grade nickel supply, the introduction of affordable EV models, and an accelerated energy storage system (ESS) demand propelling its popularity over NMC.
The ESS market, albeit smaller than the EV sector, is increasingly becoming important amidst energy security challenges. ESS offers solutions for both residential/commercial storage (behind-the-meter) and utility-scale applications (in-front-of-the-meter), improving the integration of variable renewable energy sources. Projections show ESS battery demand swelling from 130GWh in 2022 to 710GWh by 2027 (40% CAGR), while global EV battery demand is expected to rise from 530GWh to 1'900GWh during the same period (30% CAGR).
Material availability remains key
Raw material prices are showing signs of stability, creating a favorable environment for battery manufacturers to restock in anticipation of potential price escalations.
Automotive OEMs, however, are looking beyond mere pricing. They're focusing on localization, diversification, and vertical integration of their supply chains to mitigate potential fallout from macroeconomic uncertainties and geopolitical instability. Noteworthy examples include Tesla, who broke ground on a lithium refinery plant in Texas, and Hyundai, who has formed a joint venture with SK Innovation to secure a stable battery supply in the U.S. In addition, General Motors has announced a substantial multi-billion dollar investment to expand U.S. battery manufacturing in collaboration with Samsung SDI.
Contrary to initial expectations that Korean players would primarily benefit from the U.S. market, Chinese companies are also increasingly making inroads. To fully capitalize on IRA subsidies, Chinese battery manufacturers are willing to collaborate with local players, going as far as merely licensing their technology without retaining any ownership in the battery factory, as demonstrated by the Ford-CATL model. Further details on IRA's domestic content requirements will shape the future direction of Chinese players in the U.S..
Improving sector sentiment in China
The early part of the year saw a drop in Chinese EV sales as the government wound down its national subsidy program. This resulted in battery manufacturers slowing down production to clear their inventory, negatively impacting the entire supply chain. Simultaneously, some car OEMs (e.g., Tesla) chose to reduce prices to maintain sales volumes, adding more pressure on margins. Furthermore, some OEMs delayed their battery purchases until after the initial months of the year, waiting for annual price negotiations to be finalized.
However, as of May, China, the world's largest EV market and representing about half of the global demand, has seen a revival in car sales. Battery manufacturers are operating again at full capacity, and inventory levels are back to a bare minimum. With the anticipation of heightened demand in Q3, battery manufacturers may start stockpiling 1-2 months ahead of peak season, which should re-energize the supply chain and rekindle activity for all the upstream players.
The green mile shift
Sales of electric vehicles: deceleration in China, acceleration in the U.S.
Over the last two years, China has seen a swift surge in EV sales, reporting a YoY growth of 151% in 2021 and 96% in 2022. Originally, the Chinese government's target was to reach a 25% penetration rate of EVs in new car sales by 2025. However, this milestone was surpassed as early as 2022. While growth is anticipated to continue at a respectable rate of approximately 25% YoY in 2023, the recent slowdown has influenced the battery supply chain, with battery manufacturers temporarily scaling back production and purchases of upstream components.
In contrast, the U.S. EV market, buoyed by generous incentives included in the IRA and new model cycles from OEMs, is predicted to skyrocket with a YoY growth of over 60%. From a modest penetration of 7.6% in 2022, EV sales are projected to approach nearly 28% of new cars by 2026.
Closing the gap in EV pricing
The topic of price parity between electric and combustion engine vehicles can be complex as it varies across car models and sizes, countries, and subsidy programs. Broadly speaking, electric vehicles are anticipated to achieve up-front price parity with comparable combustion engine vehicles, without subsidies, across most segments by the end of the decade.
However, as has been noted, the upfront costs of vehicles aren't the primary driver of EV demand. Factors such as model availability, driving range, the extent of charging infrastructure and charging time are becoming increasingly significant. These factors have been steadily improving, and although the growth rate of EV sales is normalizing in certain regions depending on their position on the adoption curve, the sale of internal combustion vehicles peaked in 2017 and has been in long-term decline. In the meantime, Tesla's model Y has become the world's best-selling car in Q1 of this year.
Performance and efficiency as competitive differentiators
With increasing competition in the EV industry and carmakers lowering prices to secure or maintain market share, the performance of the vehicle becomes increasingly critical. The battery is undeniably a crucial component of an EV, largely determining the vehicle's driving range. Other elements such as charging time and battery lifespan also play an essential role.
Beyond battery advancements, EV powertrains are also enhancing power density by utilizing silicon-carbide (SiC) power switches, particularly in onboard chargers (OBCs) and traction inverters in powertrain systems. While SiC's adoption in EV power electronics is still in its infancy, its penetration is expected to expand rapidly, driven by the ongoing pursuit of performance improvements in EVs.
Keep shining
Decline in input costs
The cost of sea freight is now lower than it was in early 2020, and the prices of steel, aluminum, and copper have returned to pre-pandemic levels. The polysilicon market is projected to tip back into oversupply in 2023, with expected silicon Photo Voltaic (PV) module production exceeding 600GW, compared to the anticipated demand of 344 GW.
The decrease in input costs is likely to be mirrored in the price of modules, which are expected to drop from $0.21/W to approximately $0.17-0.18/W by the end of the year. This price reduction should facilitate further adoption of this technology.
Greater regulatory clarity
As previously discussed, last year the sector was impacted by a number of policy-related uncertainties, such as the anti-dumping and countervailing duties (AC/CVD) investigation, the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLA), California's new Net Energy Metering (NEM 3.0) regulation, and the erstwhile Build Back Better Act, which has evolved into the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
Presently, most of these uncertainties have been resolved: NEM 3.0 has been in effect since April, the AC/CVD investigation has been postponed, and the UFLA has resulted in an increase in polysilicon production outside of the Xinjiang region.
In addition, the U.S. Department of Treasury and IRS recently released awaited guidance on the domestic content adders for the IRA. To qualify for these adders, projects must adhere to certain sourcing requirements for numerous components in solar systems, ranging from iron and steel to solar modules, trackers, and inverters. With the guidance now clearer, we anticipate a ramp-up in U.S. manufacturing, which should stimulate a demand uptick.
Unexpected strength in utility-scale market
In our 2023 outlook, we highlighted the importance of residential-scale solar as a means to enhance energy security in a context of escalating geopolitical tensions and rising electricity costs.
While demand for residential solar solutions has stayed robust over the past few years, the often-underestimated utility-scale sector has shown resilience and experienced a rebound. Recessionary fears and a mild winter had a more significant impact on residential demand, whereas the utility-scale sector proved to be more robust. Moreover, many utility-scale projects that were delayed in 2022 due to policy uncertainty or high steel prices are now finally being executed.
Watt wizardry
Investments still lacking
Underinvestment in grid infrastructure continues to pose a global challenge, not only for the rapid adoption of new wind and solar PV capacities, but also for maximizing the power generation potential from existing installations. China's significant investments in grid infrastructure, such as increasing interconnection capacities between provinces rich in wind and solar resources and regions with high load demands, have enabled the country to considerably reduce variable renewable energy (VRE) curtailment from 16% in 2012 to less than 3% last year.
Investments in electric grids have oscillated around the $300bn mark over the past decade. However, to align with climate targets these investments would need to double to $600bn annually through 2030.
Resilience amid market volatility
The grid infrastructure sector exhibits more resilience than other consumer-driven sectors within the cleantech space, being more influenced by governmental goals. Beyond facilitating greater integration of renewables, smart grid technologies can enhance power usage, boost efficiency, enable broader electric vehicle integration, and strengthen infrastructure security.
Digital technologies remain a key focus area, both at the transmission and distribution levels, with solutions encompassing smart meters, substation automation, and network digital twins.
Continued emphasis on electrification
The transition from fossil-based processes to green electricity leads to an increase in infrastructure expenditure during the transition period. There will be a greater number of electrical products (low and medium voltage), higher electricity loads, more load variability, and an increasing demand for smart control to effectively manage distributed generation.
The smart grid sector remains central to our strategy, benefitting from the increased adoption of almost all technologies, ranging from solar PV and wind, to electric vehicles, and HVAC.
Harnessing the whirlwind
A recovery year in wind energy
Over the past two years, the global wind energy sector has faced challenges with decreasing installations from 95.3GW in 2020, to 93.6GW in 2021, and further down to 77.6GW in 2022. The industry experienced construction delays, supply chain issues, inflation, and in some instances, impairments due to Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Increased raw material costs also led to fewer order intakes. However, we predict that the sector will recover this year with new wind power installations reaching 115GW, spurred by supportive policy measures in major markets such as the USA, China, Europe, and India, as well as an easing of supply chain difficulties.
China's continued leadership
China is anticipated to maintain its position as the largest market for wind energy, representing 52% of new installations in 2023. Beyond its domestic market, China's advancements in turbine components and competitive pricing have led Chinese companies to make inroads into the global market. China is not only a global leader in wind turbine manufacturing but also a prime production hub for key components and raw materials. It operates over 100 of the world's 153 nacelle assembly facilities with an additional 64 under construction. It also dominates the global supply chain for casting, forgings, slewing bearings, towers, and flanges, holding a market share of over 70%. In terms of rare earth materials, which are used in permanent magnets, China is responsible for 68% of the mining and 94% of the processing.
Offshore wind: the rapid growth segment
Due to advancements in offshore wind technology—particularly improved foundations allowing turbines to be placed further offshore in deeper waters to capture more wind—offshore wind power is attracting increasing attention. Offshore wind installations are projected to double from 9GW in the previous year to 18GW in 2023, with China and Europe anticipated to drive this growth, contributing to over 80% of new installations in the next two years. Companies like Orient Wires & Cables, a manufacturer of submarine cables, are well-positioned to capitalize on the offshore wind sector's expansion in China.
Living-energy elixir
Biofuel demand continues to grow
As we cross the mid-year threshold for 2023, the demand for biofuels continues to gain momentum across the globe. Influenced by mounting environmental concerns and sustainability targets, countries are increasingly leaning towards biofuel consumption (global biofuel demand is expected to grow 20% in the next five years). Key consumer nations like the United States, Brazil, and the European Union are leading the charge, with significant strides made towards biofuel adoption, helping mitigate the climate impact of their transport sectors. Yet, these countries are grappling with an imbalance between escalating biofuel demand and supply constraints, thereby causing price fluctuations. Additionally, supply chain disruptions caused by geopolitical events and weather-related factors add another layer of complexity to the market dynamics.
Feedstocks encounter supply-demand imbalance and price volatility
On the feedstock front, primary inputs for biofuel production such as corn, soybeans, and sugar have seen their prices undergo changes due to various factors. In the United States, corn and soybean oil prices are exhibiting signs of a minor decline, though the escalating demand for renewable diesel and limited growth in soybean oil supplies moderate this effect. In contrast, countries like Brazil and India are grappling with high sugar prices, exerting upward pressure on ethanol costs. Meanwhile, the European Union benefits from increased imports of advanced biofuels and feedstocks such as used cooking oil from China, leading to more affordable biodiesel. However, supply pressures persist, making feedstock diversification an imperative for long-term biofuel production sustainability.
Aviation sector navigates challenges
The aviation sector remains a significant focus area in the push for biofuel adoption. In the face of global pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, airlines are turning to biojet fuels as a cleaner alternative. However, the sector has faced headwinds due to high biofuel prices and supply limitations. Current penetration of the so-called Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) remains quite low (still below <1%). The entrance of unconventional feedstocks into the production landscape, such as used cooking oil and agricultural residues, is a promising development. Although these alternative feedstocks currently constitute a small fraction of total biofuel production, the pace of innovation is fast, and we are witnessing an increasing number of projects harnessing these resources. Yet, industry stakeholders must step up their efforts to avoid a potential supply crunch, accelerate the pace of change and meet the burgeoning biofuel demand in the aviation industry.
Architecture of efficiency
The imperative for decarbonization
The building sector continues to be a pivotal player in the global energy consumption landscape, contributing to 30% of worldwide energy demand and 27% of total energy-related emissions in 2021. This contribution is even higher, reaching 33%, when incorporating the energy expenditure for the production of construction materials like cement, steel, and aluminum. In light of increasing concerns over energy security, there has been an intensified focus on implementing measures to curtail buildings' energy demand. Such strategies encompass retrofitting heating and cooling systems with heat pumps, enhancing building insulation, optimizing appliance efficiency, and encouraging energy-saving behavioral adjustments. The building sector remains a key battlefront in the pursuit of decarbonization, reinforcing the urgency to accelerate energy-saving initiatives within this industry.
Heat Pumps market: building momentum and scaling heights
Global heat pump sales showcased a remarkable advance, growing at a rate of 11% in 2022. This development, charting the second year of double-digit expansion, signifies the substantial role of heat pumps in transitioning to a secure, sustainable heating future. A combination of high natural gas prices and intensified efforts to curb greenhouse gases has led to enhanced policy backing and benefits for heat pumps, triggering their widespread adoption. Europe emerged as a trailblazer, registering a 40% spike in heat pump sales, with air-to-water models leading the pack with a 50% rise. In the US, the preference for heat pumps surpassed that of gas furnaces, while the world's largest market, China, remained steady amidst macroeconomic slowdown.
Currently, heat pumps supply approximately 10% of global heating needs, covering over 100mn households. To achieve the global energy and climate targets, heat pump deployment needs to fulfill nearly 20% of the global heating requirements by 2030. To reach net-zero emissions by 2050, sales would need to expand by over 15% per year within this decade.
Installation of heat pumps is currently focused on new buildings and single-family homes. For continued growth, energy efficiency retrofits and attention to multi-story residential and commercial spaces will be necessary.
Resilience amidst complexity
Although decarbonizing the building industry has been historically complex, 1H23 has shown a more resilient trend than previously expected within the smart building sector. The prolonged renovation cycles are finally starting to demonstrate a trend shift, largely influenced by government regulations and policy changes.
While consumer sentiment has a role to play, it is government policies that are providing a more significant push. Policymakers' focus on carbon reduction and energy efficiency has steered the industry towards renovation initiatives that lead to greener and smarter buildings.
The renovation and retrofit process, despite being time-consuming and resource-intensive, is now being perceived as a necessary investment for future energy independence. It is clear that the drive towards a more sustainable future has begun to influence the building industry's strategic planning and operational focus.
Liquid lifeline
The ongoing relevance of water amid climate change
Climate change has precipitated an era of profound transformation, significantly impacting global water systems. Droughts are becoming more frequent and severe, while flooding events are escalating in frequency and intensity. These shifts reshape the water landscape, necessitating a more robust and strategic approach to managing water resources. A secure, reliable water supply is not just a question of sustainability; it's a matter of survival for ecosystems and economies alike. As such, the strategic importance of water within the broader climate change conversation cannot be overstated.
Water market developments: policy shifts and mergers
The first half of this year has been marked by dynamic changes in the water industry, propelled by political decisions and key business consolidations. Last April, the Biden Administration announced a specific $85mn investment plan in clean water infrastructure. This move, despite its limited funding focusedo only on the Mid-Atlantic region, underscores a renewed commitment to sustainability and mitigating water scarcity at the policy level.
On the business front, the water sector is seeing considerable consolidation. The notable acquisition of Evoqua by Xylem is a case in point. The $7.5bn deal is set to reshape the sector by creating one of the world's largest water companies. With an anticipated annual revenue exceeding $7bn and over 22'000 employees, the new entity is poised to offer a broader suite of products and services, enhancing its ability to meet the complex needs of the global water market.
Innovative technologies to tackle water scarcity
As water scarcity intensifies, technology is stepping up as a formidable tool in our arsenal. Technological innovation, specifically in the water sector, has accelerated. We're seeing major advances in desalination processes, which have made significant strides in reducing costs while increasing efficiency. Meanwhile, digital technologies, such as IoT, are being harnessed to improve water usage, distribution, and maintenance. Smart meters and sensors are now commonplace, delivering real-time data to inform decision-making and reduce wastage. These digital solutions are also playing a crucial role in mitigating the impact of aging infrastructure, from leak detection to predictive maintenance. As we continue to lean into these technological advances, they will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in helping us navigate the mounting challenge of water scarcity.
The power promise
Europe advances in supporting Hydrogen while the U.S. fiddles with uncertainty
European fiscal support is strengthening with initiatives like the European Hydrogen Bank, slated to hold green premia auctions for Green H2 projects. Additionally, Germany's recent move to link its H2Global support scheme to the H2 Bank could significantly amplify funds for green hydrogen investment.
In contrast, the U.S. faces uncertainty awaiting guidance on the 45V hydrogen production tax credit from the Treasury. The anticipation is that this guidance, expected to be released by this autumn, could be lenient towards hydrogen producers, thus unlocking planned Green H2 projects
Blue hydrogen gains traction
There's a rising focus on blue hydrogen, particularly in North America. Blue hydrogen is produced from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming (SMR), which is combined with carbon capture and storage (CCS). This contrasts with green hydrogen, produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy, which is generally considered more environmentally friendly but is still grappling with technological, supply chain, and regulatory challenges.
Major industrial gas producers, such as Air Products and Linde, are progressing with significant blue hydrogen projects worth over $1bn each. Many of these large-scale commercial projects, projected to start output between 2024-2026, indicate growing corporate confidence in blue hydrogen's market potential and its role in satisfying the increasing demand for low CO2 hydrogen and ammonia.
Scaling green hydrogen production remains a challenge
Over the last 18-24 months, the hydrogen industry has experienced setbacks as electrolyzer OEMs grappled with the challenges of transitioning from small tech-focused companies to large-scale, reliable manufacturers. The pressure to upscale projects from 20-30MW to over 100MW led to a series of profit warnings, impacting the industry's growth trajectory.
However, the industry's shift in focus toward operational efficiency is starting to show promising signs. Companies like ITM Power and Plug Power have improved their production capabilities, indicating a steady recovery in the industry. Despite these improvements, profitability remains elusive, underlining the early-stage nature of the industry.
Scaling green hydrogen production further will require a more holistic approach, focusing on the broader value chain. The sector would benefit from greater OEM and supply chain maturity, simpler regulation, and more public fiscal support to accelerate green hydrogen investment.
Harvesting the future
Continued importance of food and agriculture in the climate crisis
The critical role of food and agriculture in climate change continues to be a dominant theme. It remains apparent that the food industry, responsible for over 33% of global greenhouse gas emissions and utilizing approximately half of the world's habitable land, is one of the most significant contributors to the global climate crisis. Livestock rearing alone consumes 75% of agricultural land. As we grapple with the urgent necessity of mitigating climate change, it is more crucial than ever to address the substantial environmental footprint of our food systems.
A tech-driven transformation is on its way
Encouragingly, the food and agricultural systems are witnessing a profound transformation, with sustainability and profitability driving this change. At the core of this evolution lies technology, offering a suite of innovative solutions that range from farm automation to precision agriculture, alternative proteins to green agrochemicals, and regenerative agriculture practices. Farm automation, for instance, reduces the impact of farming on climate change and helps farmers adapt to its financial implications. Simultaneously, regenerative agriculture practices aim to restore soil health, capture carbon, and rebuild rural economies. Similarly, advancements in alternative proteins and green agrochemicals are offering more sustainable options for food production. Thus, technology is becoming an indispensable ally in achieving a balance between profitability and sustainability.
Overcoming barriers in alternative proteins adoption
The transition from animal proteins to alternative ones is not as swift as initially anticipated. Despite the strong environmental rationale behind the shift, the market for alternative proteins is still in its early stages, and changing consumer habits takes time. Today, plant-based protein products represent less than 1% of the total food market, suggesting that mass adoption is still a distant reality. Even as traditional food and beverage companies join the alternative meat market, it is crucial to understand that breaking age-old nutritional habits and convincing consumers about the health benefits and taste equivalency of these products is a long-term process. While progress is steadily being made, the time frame for this major dietary shift remains unclear.
The atomic leap
Key to the energy transition
The ongoing energy transition has underscored the indispensable role of nuclear power in achieving global decarbonization goals. As the world strives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, nuclear energy has emerged as a pivotal player, offering a reliable, dispatchable, and scalable low-carbon power source. Renewables such as solar PV and wind are intermittent by nature and cannot provide consistent power around the clock. Therefore, the combination of renewable energy with the dependable output from nuclear power plants is seen as a practical solution for a steady, low-carbon energy supply. Nuclear currently provides about 10% of global electricity, a share that is likely to hold steady or even increase as the energy transition unfolds.
Growing government support globally
Global policy shifts have also begun to favor nuclear power, with supportive measures being adopted by some of the world's largest economies. In the United States, the administration's decarbonization plans acknowledge the importance of nuclear energy, while in the European Union, the recent inclusion of nuclear in its Taxonomy for sustainable economic activities has opened new investment avenues. Meanwhile, China continues to lead the way in terms of nuclear power development, with the country committed to growing its nuclear capacity as part of its broader low-carbon energy strategy. This policy support, across multiple major markets, is creating a fertile environment for the expansion of nuclear power.
Overcoming costs and time challenges
Despite this positive momentum, significant challenges persist. Construction costs and timeframes remain substantial obstacles to the widespread adoption of nuclear power. Traditional nuclear power plants are expensive to build and commission, and their construction often faces delays. However, innovation in the form of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) could be a game-changer. These units promise lower capital costs and shorter construction timelines, as well as enhanced safety features and less nuclear waste. If these promises can be realized, SMRs could help overcome the economic and temporal barriers currently hindering the nuclear industry. As we move further into 2023 and beyond, the success of these new technologies will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of nuclear energy and its contribution to a sustainable energy mix.
Reclaiming tomorrow
The scale-up challenge
Carbon capture technology is increasingly becoming an important element in the global push towards decarbonization, particularly for hard-to-abate sectors. Current solutions fall short of making a substantial dent in carbon emissions, with only 35 commercial carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) facilities capturing 45Mt of CO2 per annum compared to climate objectives requiring ~1.7Gt of CO2 capture annually. Clearly, scaling up carbon capture operations is a pressing issue, but only a handful of pure players in this field are listed.
Variable costs and efficiencies
CCUS technologies, while diverse in nature, are united by their objective to capture and either store or utilize CO2 emissions. Advances have been seen in Direct Air Capture (DAC), an innovative technique that pulls CO2 directly from the atmosphere. However, costs for carbon capture differ vastly based on the CO2 concentration and the method utilized. Depending on these factors, costs can range between $40 to $400 per ton of CO2. As technology advances, new projects and investments could potentially decrease these costs, contributing to broader CCUS adoption. The challenge and opportunity lie in selecting and backing the most promising of these technologies, with an eye on their economic feasibility.
The power of policy
Governmental support and policy interventions are playing a crucial role in driving the adoption of CCUS technologies. A wave of new regulations and incentives are set to roll out across the globe, with countries like Malaysia, Indonesia, India, Japan, Thailand, and China advancing their CCUS frameworks. Meanwhile, in the U.S., policy advancements like the Inflation Reduction Act are expected to fuel further CCUS projects in 2023. The private sector, too, isn't idle, with the Chevron-Talos-Carbonvert and E.ON-Horisont Energi deals suggesting an impending M&A flurry as companies vie for positions in key CCUS hubs. Hence, policy backing and market developments suggest that the CCUS sector is making progress, although there is still a significant need to catch up in terms of growth and adoption.
Cycle of renewal
The emerging challenge of cleantech waste management
The proliferation of clean technology has significantly accelerated over the past decade, yielding an unprecedented number of solar panels, wind turbines, electric vehicles, and lithium-ion batteries. As we move towards a more sustainable future, the lifespan of these technologies is also reaching an inflection point, necessitating appropriate measures to manage end-of-life clean tech waste. Discarded solar panels, depleted batteries, and obsolete wind turbines pose substantial environmental risks, which need to be mitigated through effective recycling and waste management strategies. For instance, it's estimated that by 2030, there will up to 8mn metric tons of retired solar panel waste globally and some 12mn tons of lithium-ion batteries will reach their end of life.
Scaling up recycling and repurposing in clean tech
The industry is at an early developmental stage in confronting these challenges. The focus is not only on recycling these materials, but also on repurposing them for secondary use. This approach includes refining manufacturing processes to enhance the recyclability of clean tech products. For instance, manufacturers are rethinking the use of adhesives that make recycling more complex. While innovative solutions are gradually emerging, they need to be scaled up significantly. Companies like Li-Cycle and Redwood Materials are pioneering new methods, but policy interventions are required to make recycling costs competitive with the market value of recovered metals.
Balancing mining and recycling
Despite these promising developments in recycling and reuse, the complete elimination of mining is not viable. At best, effective recycling can mitigate mining requirements and foster a level of independence, but the demand for raw materials is still expected to rise. According to some estimates, recycling could provide 12% of the global cobalt demand, 7% of nickel, and 5% of lithium and copper.
To achieve the ambitious sustainability targets set worldwide, the extraction of raw materials will remain a necessity. A more sustainable approach would be to integrate mining, recycling, and reuse practices into a comprehensive circular economy model, creating a more sustainable lifecycle for clean technology.
Year’s favourites 2023 – An update
SolarEdge
(SEDG US)
We've chosen SolarEdge as our top pick for the year due to its dominant presence in the residential inverter sector, the escalating demand for residential solar solutions amid the energy security crisis, and the company's expanding foothold in the energy storage market. We also anticipated a decline in input costs and transportation/logistics expenses to favorably impact profit margins.
So far, the company has reported robust results and issued an earnings guidance that surpasses expectations, attributed to its geographical diversification and significant exposure to a strong commercial and industrial (C&I) demand.
SolarEdge's Q1-2023 revenues showcased an impressive growth of 102% YoY in Europe and 32% YoY in Rest of the World (RoW), more than compensating for the 4% YoY decline in the US.
Looking ahead to the second half of the year, we anticipate that SolarEdge will sustain this momentum. As the company's performance continues to improve and margins recover, we foresee a subsequent revival in the stock, reflecting these positive dynamics.
Wolfspeed
(WOLF US)
Wolfspeed aimed to capitalize on the growing adoption of Silicon Carbide (SiC) devices by electric vehicle manufacturers. However, the company has encountered execution challenges, primarily due to the transition to taller 150mm boules at their Durham facility and a slower-than-expected ramp-up at their 200mm Mohawk Valley factory. These hurdles have contributed to unforeseen gross margin pressures.
As the pioneer in navigating the transition to the 200mm format, Wolfspeed is facing these unique growth-related challenges head-on. Despite these hurdles, our long-term confidence in SiC and Wolfspeed's technological leadership remains unshaken. However, we are keenly waiting for more positive data points, especially regarding execution.
As we look toward the latter half of the year, we anticipate that once these initial challenges are overcome, Wolfspeed is poised to reap the rewards of its innovative approach.
Samsung SDI
(6400 KS)
Samsung SDI remains a standout pick this year, affirming our belief that the company's robust position in the battery market sets it up for substantial growth. Anchored by its innovative array of battery solutions and strong partnerships, Samsung SDI has been strategically positioning itself to capitalize on the global shift toward electric vehicles. As per recent updates, the company's storyline is unfolding as anticipated. Its sustained focus on addressing the burgeoning demand in the European and American markets has paid off, with no signs of slowing down.
Despite some concerns over small battery and electronics materials in the near term, Samsung SDI's mid-to-long term outlook remains favorable. As it moves toward a more US-focused strategy post-2025, the company's ability to capitalize on its wide-ranging portfolio and JV partnerships indicates a promising trajectory. Hence, the narrative of Samsung SDI as a leading player in the EV battery space remains compelling, and the company continues to exhibit strong performance, indicating a potentially rewarding path ahead for investors.
Catalysts
China's recovery. China's recovery is poised to eventually materialize, particularly within the battery sector where manufacturers have already signaled a boost in production and an end to inventory de-stocking activities
Government plans taking shape. We anticipate further guidance on major initiatives such as the IRA, which should enhance market visibility and unveil new opportunities for domestic manufacturers
Stabilization of raw material prices. Particularly in the solar PV industry (polysilicon) and battery materials sector, this trend is expected to alleviate margin pressures.
Risks
Geopolitical tensions. The escalating tensions between China, the West, and Taiwan bear potential to disrupt supply chains and impact the manufacturing sector across various cleantech segments.
Greenflation concerns. Inadequate supply of critical resources might intensify cost inflation, thereby reducing the appeal of clean technologies.
Global economic downturn. Should a global recession materialize, it would negatively affect consumer demand and could slow the uptake of consumer-centric clean technologies, such as electric vehicles and residential solar panels.
Companies mentioned in this article
E.ON (EOAN); General Motors (GM); Hyundai (005380); Linde (LIN); Orient Wires & Cables (603606); SK Innovation (96770); Samsung SDI (006400); SolarEdge (SEDG); Tesla (TSLA); Wolfspeed (WOLF); Xylem (XYL)
Sources
- Can you really go green without China?
- Charge or die – which battery is the best?
- Electric Vehicle Outlook 2023, BNEF
- Ford and CATL charge ahead with a $3.5bn battery plant deal
- Global heat pump sales continue double-digit growth
- Outlook 2023 - Sustainable Future: Energy security to fuel the energy transition
- The biggest climate investment in U.S. history
- Buildings Tracking report 2022, IEA
- Global Wind Report 2023, GWEC
- Investment spending on electricity grids, 2015-2021
- Solar: The big winner of the global energy shock
- The coming carbon capture and storage boom – we have lift off
Explore:
Disclaimer
This report has been produced by the organizational unit responsible for investment research (Research unit) of atonra Partners and sent to you by the company sales representatives.
As an internationally active company, atonra Partners SA may be subject to a number of provisions in drawing up and distributing its investment research documents. These regulations include the Directives on the Independence of Financial Research issued by the Swiss Bankers Association. Although atonra Partners SA believes that the information provided in this document is based on reliable sources, it cannot assume responsibility for the quality, correctness, timeliness or completeness of the information contained in this report.
The information contained in these publications is exclusively intended for a client base consisting of professionals or qualified investors. It is sent to you by way of information and cannot be divulged to a third party without the prior consent of atonra Partners. While all reasonable effort has been made to ensure that the information contained is not untrue or misleading at the time of publication, no representation is made as to its accuracy or completeness and it should not be relied upon as such.
Past performance is not indicative or a guarantee of future results. Investment losses may occur, and investors could lose some or all of their investment. Any indices cited herein are provided only as examples of general market performance and no index is directly comparable to the past or future performance of the Certificate.
It should not be assumed that the Certificate will invest in any specific securities that comprise any index, nor should it be understood to mean that there is a correlation between the Certificate’s returns and any index returns.
Any material provided to you is intended only for discussion purposes and is not intended as an offer or solicitation with respect to the purchase or sale of any security and should not be relied upon by you in evaluating the merits of investing inany securities.

